In the dynamic realm of dragon fruit cultivation, where sustainability meets innovation, the compatibility of microbial pest control with other practices is a topic of profound significance. As farmers strive to adopt holistic approaches to pest management, understanding how microbial solutions harmonize with existing practices becomes paramount. Let’s delve into the intricate interplay between microbial pest control and other agricultural practices, unveiling a tapestry of synergy and sustainability.
Table of Contents
Exploring the Compatibility of Microbial Pest Control with Other Practices in Dragon Fruit Cultivation
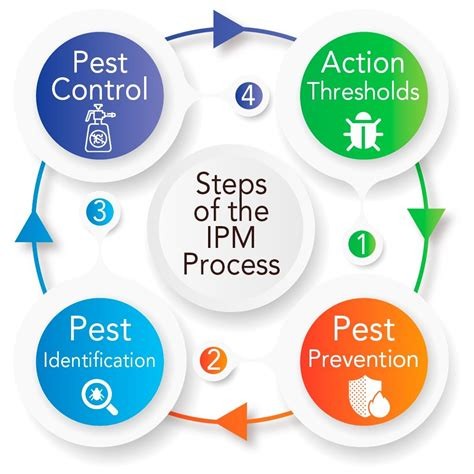
1. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Microbial pest control aligns seamlessly with the principles of Integrated Pest Management (IPM), a holistic approach that emphasizes the integration of multiple pest control strategies. By combining microbial agents with cultural practices, biological controls, and judicious use of synthetic pesticides, farmers create a robust defense against pests while minimizing environmental impact and preserving natural ecosystems.
2. Crop Rotation and Diversity
The compatibility of microbial pest control with crop rotation and diversity practices underscores its versatility in diverse agricultural systems. By rotating dragon fruit crops with complementary species and incorporating cover crops, farmers disrupt pest life cycles, reduce pest pressure, and create habitat diversity for beneficial organisms. Microbial agents complement these efforts by providing targeted pest control without disrupting the ecological balance.

3. Organic Farming Practices
For farmers adhering to organic farming principles, microbial pest control serves as a cornerstone of pest management strategies. Unlike synthetic pesticides prohibited in organic production, microbial agents such as Bacillus thuringiensis and Beauveria bassiana offer effective, natural alternatives that align with organic certification standards. Their compatibility with organic farming practices ensures compliance with regulatory requirements while promoting ecological sustainability.
4. Pollinator Protection
The compatibility of microbial pest control with pollinator protection practices highlights its role in fostering biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. Unlike broad-spectrum pesticides that indiscriminately harm beneficial insects, microbial agents specifically target pest species, minimizing collateral damage to pollinators such as bees and butterflies. Integrated pest management approaches that prioritize pollinator protection synergize with microbial solutions, promoting a harmonious coexistence between agriculture and biodiversity.

5. Soil Health and Fertility Management
Microbial pest control practices contribute to soil health and fertility management by minimizing the reliance on synthetic pesticides and reducing soil contamination. Unlike chemical pesticides that disrupt soil microbial communities, microbial agents support beneficial soil microorganisms, enhancing nutrient cycling, soil structure, and overall fertility. Integrated approaches that integrate microbial pest control with soil conservation practices promote long-term sustainability and resilience in dragon fruit cultivation.
6. Water Conservation and Management
In regions where water scarcity is a pressing concern, the compatibility of microbial pest control with water conservation and management practices becomes particularly relevant. Unlike conventional pesticide applications that may require significant water usage for dilution and application, microbial agents can be applied in lower volumes, reducing water consumption and minimizing environmental impact. Precision irrigation techniques that optimize water use further enhance the compatibility of microbial pest control with water conservation efforts.
Conclusion: Synergy in Sustainability
In the intricate web of agricultural practices, microbial pest control emerges as a linchpin of sustainability and ecological resilience. Its compatibility with integrated pest management, organic farming principles, pollinator protection, soil health management, water conservation, and other sustainable practices underscores its versatility and efficacy in modern agriculture. By embracing microbial solutions alongside complementary practices, dragon fruit farmers pave the way for a harmonious and sustainable future, where innovation and tradition converge in the pursuit of agricultural excellence.
